Below we describe in detail the parts of this multifunctional test strip from right to left.
1) Print fine dot control section. Divided into 6 grids in the 5×6mm format, the grids are arranged in order of 0.5%, 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, and 5% fine dots in 150L/inch grids. The feature is that the 0.5 to 5% print spot fineness detection segment and the micro-printing plate resolution cross-over measurement segment cooperate to serve as a control element for detecting the exposure of the metal plate printing plate, and the printing plate is controlled according to the quality requirements of different printing products. The percentage of fine dot reproduction.
2) Neutral gray balance observation section. In the area of ​​15×6mm, each color is arranged in three sections, ie, yellow, magenta, and cyan, consisting of 25%, 50%, and 75% dots of 150L/inch to identify the copying effect of the proof and print gray balance. .
3) Overprinting and color mark detection section. In the area of ​​30 x 6mm is divided into six kinds of hue, namely yellow, red, magenta, cyan, green. Each color is a solid density or an overlay color scale used to determine the percentage of overprint for each color ink. The monochromatic density of the ink can also be determined.
4) Black density three-color reduction section.
1 yellow, magenta, and green solid overprint three-color black;
2 yellow, magenta, cyan, and black solid four-color black;
3 monochrome black solid.
5) Five-segment weight point test (Brunner's second-generation test strip section).
1 field: used to determine the density of the ink layer;
2275% of coarse mesh (30L/inch) segments;
3375% fine mesh (150L/inch) micrometer section;
4450% coarse mesh (30L/inch) segment;
550% fine mesh (150L/inch) micrometer section.
Note: 50% coarse, fine dot and 75% coarse and fine dots are all used to calculate the printed dot gain value. This method is simple, fast and accurate and is suitable for on-site management.
6) Fine mesh micrometers (Brunner's second generation test strips).
As shown in FIG. 3, the outer corner of each 1/4-grid is composed of a 6-line/mm equal-width fold line, which is used as a mark for checking whether the halftone dot is deformed or ghosted during printing.
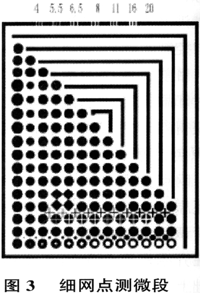
1 There are 13 outlets in the first row near the horizontal line of the grand crucifix, and the outlets on the innermost side are the actual outlets. The 12 outlets in order are 1.5%, 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5% respectively. ,8%,
10%, 12%, 15%, 20% hollow points; and the actual number of points with the same number and dot area between the second row of real points; the third point of the network point on the inner side is also a solid point, but From the second network point, the exact same area as the next two lines is taken out. The difference is that the screen points are represented by the shade cross mark; at the same time, they are the positive cross marks that take the same area and number, and are clamped in the corresponding positions.
According to the yin and yang network points and the cross yin and yang signs, the exposure of the printing plate can be judged, and the change of the dot transfer can be identified. The horizontal expansion of the dot, the vertical bar of the cross mark becomes thicker, and the yin vertical line becomes thicker; the vertical direction is the same.
Based on this, we can also directly look at the direction of network changes and the percentage of outlets. If 10% of the negative cross mark disappears, the 12% negative cross mark retains the horizontal line, and the 15% vertical line remains. This indicates that the horizontal increase of the dot is within 12%, and the longitudinal increase is within 15%.
2 There are four 50% square points at the center of the inner side of each 1/4 image, which is used to control the depth of the layout when printing, proofing or printing. If the angle of 50% dots is large, it means that the printing plate is too tanned or the printing ink is excessive, the image is deep, and the dot enlargement value is large; if the 50% dots are separated, the image is shallow and the dots are reduced.
3 The area of ​​the two rows of juxtapositions along the vertical direction of the large reticle is different. The first row gradually expands from the bottom up to the area where 13 meshes are 75%; the second row gradually decreases from the bottom up until the first Thirteen outlets have an area of ​​25%. The total area of ​​two outlets corresponding to two rows is 100%.
4 On the upper and lower edge lines, a super-fine test mark is arranged, and there are different widths of the negative wire for measuring the resolution of the printing plate, which is divided into 4, 5î€5, 6î€5, 8, 11, 16, 20 μm.
Here we need to point out that the densitometer used for measuring Bruner's control strip system is a narrow-band densitometer with an aperture diameter of 4 mm. Both the MacBeth manual densitometer and the MacBeth scanning densitometer can be used to measure Bruner systems.
At present, in some countries where the printing industry is developed, instrument testing of test strips has been developed to computer program control. Heidelberg and Roland Corporation took the lead in the use of computer program control devices to automatically control ink transfer, water transfer, adjustment overprinting, and printing plate inking volumes. The application of the density determination memory storage system allows the operator to perform remote control completely on the console.
As an effective measure of printing quality control, printing measurement and control strips are not widely used in our country. However, with the integration of the entire industry with the world, the use of printing quality control strips to control printing quality is bound to become a trend.
Copier Toner,Best Ricoh Printer Toner,Newly Ricoh Printer Cartridge,Ricoh Printer Toner
jiangmen jinheng office equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.jmjhtonercartridge.com