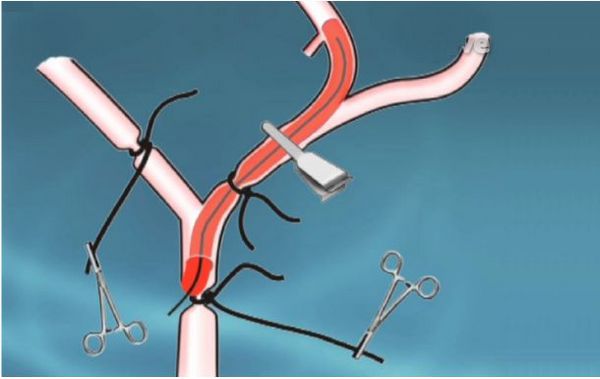
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) is currently the most commonly used model of focal cerebral ischemia. The MCAO model first blocks the external carotid artery (ECA) and its branches, and blocks the ptalatine artery (PPA). To cut off the blood flow of lateral accessory circulation from extracranial sources. A nylon thread was inserted from the ECA, through the internal carotid artery (ICA) to the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), and mechanically blocked the blood supply from the middle cerebral artery (MCA) to establish the middle cerebral artery ischemia model. This model can pull out the nylon thread without anesthesia to restore blood flow and achieve reperfusion. The thread embolization method has the advantages of no craniotomy, positive effect, and accurate control of ischemia and reperfusion time. It is used to study the sensitivity and tolerance of neurons to ischemia, observation of drug efficacy, and reperfusion injury and treatment time window Ideally, it also has the characteristics of low systemic impact and long animal survival time, and is suitable for the study of chronic brain injury. Controlling the variable factors can avoid the instability of the experimental results. 1. Main equipment (1) Preparation before ischemia: brain stereotaxic instrument, (mouse adapter), microsyringe pump, microsyringe, skull drill (2) Manufacture of ischemic model: gas anesthesia machine, isoflurane, stereo microscope, cold light source, operating table, postoperative incubator, brain mold, surgical instrument package (3) Evaluation of ischemic model: nerve function evaluation method (BBB score), TTC staining, pathological evaluation (4) Post-ischemic behavior detection: grip tester, rotarod ... 2. Experimental animals (1) SPF grade Wistar rats, healthy, male, weighing 250-300g. (2) SPF grade C57 mice, healthy, male, weighing 18-25g, experimental protocol and video, please click to watch and download: Click Here 3. Experimental grouping The experiment was divided into six groups: normal control group, model group, positive drug group, and test drug group in three dose groups, with 15 animals in each group. 4. Modeling method (take rat as an example) (1) Rats are anesthetized with 1.5-2% isoflurane gas, the neck is skin-prepared, disinfected, an anal temperature probe is inserted, and the body temperature is maintained at 37 ± 0.5 ℃. (2) A midline incision in the neck to expose the right common carotid artery, internal carotid artery and external carotid artery. A 6-0 silk thread was used to ligate the distal end of the external carotid artery at a distance of 4 mm from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, another 6-0 silk thread was inserted into the external carotid artery, and a slip knot was placed near the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. (3) Use arterial clips to close the common carotid artery. Cut a small opening in the external carotid artery 3 mm away from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, insert a 0.33 mm diameter nylon thread treated at the head end through the small opening, enter the internal carotid artery, and insert it into the middle cerebral artery, The insertion depth of the nylon thread is about 16 ± 1mm ​​from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. (4) Remove the thread plug 90 minutes after ischemia, ligate the proximal end of the external artery with 6-0 silk thread, suture the neck wound with 3-0 silk thread, disinfect the wound with vital iodine, place the rat on the heating pad, and wait for awake Put it in a constant temperature rearing box. (5) 24 hours after operation, the mice were scored for neurological function, and then the rats were continued to be anesthetized, and brain slices were taken for TTC staining and pathological staining. 5. Evaluation of the model (1) Signs of signs of neurological deficit Refer to the 5-point system of Longa and Bederson for scoring 24h after the animal is anesthetized. The higher the score, the more severe the behavioral disorder of the animal. 0 points: No symptoms of nerve damage 1 point: The contralateral forepaw cannot be fully extended 2 points: circle to the opposite side 3 points: Pour to the opposite side 4 points: Cannot spontaneously go away, loss of consciousness (2) TTC staining After anesthetizing the rats, the brain tissue of the rats was taken and frozen in a refrigerator at -20 ℃ for 30min and 30min. Dispose 1% TT C (W / V) in PBS, bath at 37 ℃ until TTC dissolves, slice the frozen brain tissue into 10 ml TTC solution, and incubate at 37 ℃ for 10 min at a constant temperature. Turn the brain slices from time to time to stain the tissue evenly. Normal brain is bright red after staining, while the infarct area is pale. Attachment: TTC staining effect diagram of mice after 2h of ischemia, as follows: (3) Pathological evaluation After taking the brain, fix it with 4% paraformaldehyde solution, fix it after dehydration of sucrose solution, fix it after dehydration of sucrose solution, freeze it after dehydration of sucrose solution, and embed it for frozen section. , Doing Nissl staining can be used to evaluate the infarct size. China Cookware,New Cookware Sets,Stainless Steel Cookware Fucheng Metals Production Co., Ltd. of Jiangmen City , https://www.fcmp.com