2. Resolution The red and blue color filters are arranged alternately on the chip, and their resolution should be halved, that is: Flip Chart,Magnetic Mobile Flip Chart,Alloy Flip Chart,Magnetic Flip Chart Jiangyin Europtronic Stationery Co., Ltd. , https://www.youpuwhiteboard.com
The resolution of a digital camera depends mainly on the resolution of the optical lens, the number of pixels of the sensor chip, and also on the arrangement of the color filters on the photosensitive chip.
In order to obtain color image information, the incident light must be decomposed into red, green, and blue light components and converted into electronic signals. At present, the color light decomposition technology on the photosensitive chip includes: single-layer color filter methods (RGB, RGBE, CMYG) and multi-layer decomposition methods (Foveon's X3 technology). As far as the current application is concerned, single-layer color filters are more common, and Foveon's X3 technology is less widely used. 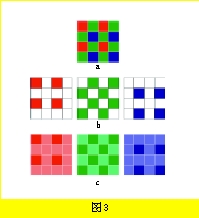
The color light decomposition method of a single-layer filter is shown in Fig. 3: Fig. 3a shows the arrangement of imaged RGB filters; Fig. 3b shows the arrangement of color filters for each channel; Fig. 3c shows the pixels actually collected (with dark colors Represents the relationship with the interpolated pixels (shown in light colors). It can be seen that since the micro-filters are arranged separately, their actual resolution is lower than the so-called “resolution†because of the four sensitized units (common RGB modes are: 1 red unit and 1 blue unit). , 2 green cells, or RGBE: 1 red cell, 1 blue cell, 1 green cell, 1 emerald cell) are combined into a single colored pixel. For each color channel, the actual image information actually collected by such a digital camera is not a complete pixel, but all the pixel data are obtained through mathematical interpolation on the basis of the collected partial pixel information.
Take the RGB method as an example. Assuming a 5 megapixel, 4:3 format digital camera, the number of horizontal and vertical pixel rows and columns of the imaging chip is 2592×1944, that is, the effective number of pixels is 5038848; the imaged face line is 1/1.8 inches, while RGB filters are staggered, as shown in Figure 3a. Assuming that the resolution of its optical imaging lens is large enough, the actual resolution of red, green, blue imaging can be calculated.
The ratio of the horizontal/vertical dimension of the imaging surface of the chip to the diagonal dimension of the chip is respectively and, therefore, 

On the chip, green filters are arranged in each row with a resolution of: 
Obviously, if the red, green, and blue light lines can be separated and collected separately, the resolution of the color can be doubled. This is the advantage of the Foveon X3 color light multi-layer decomposition method. As shown in Figure 4, the blue, green, and red signals are completely collected and taken out in layers. The number of collected pixels is the same as the nominal value. 
In a similarly configured 5 megapixel digital camera, the number of pixels is still 2592×1944, and the imaging size is unchanged. With the multi-color decomposition of colored light, the resolutions of blue, green, and red are the same: 
(to be continued)