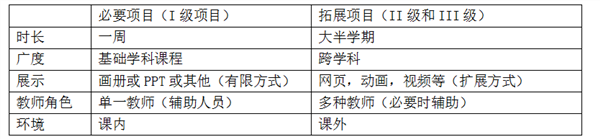
Image source: Photographed network For a long time, I have been thinking about how to carry out STEAM teaching, what kind of teaching mode to use STEAM to write something, think for a long time, and finally put forward a pen today, write some thoughts on this issue. In recent years, due to the important position of STEAM in global competitiveness, the development of STEAM education has become a top priority for all countries, and China is no exception. This is also the trend of the 21st century. Then, through STEAM teaching, students (not to mention "children", so as not to mislead readers to think that it is kindergarten or primary school) can harvest what? Summary as follows: As can be seen from the figure, students can not only learn the knowledge of textbooks, but also get the skills necessary for the 21st century. However, how do these goals are achieved? Here is an important concept that is derived from PBL (Project-Based Learning), which translates into project-based learning. As the name implies, PBL is a model for organizing students around the project. These projects have complex tasks that are based on challenging real-life issues and involve students in design, problem solving, decision making, modeling, testing, optimization, communication, reflection, and more. In a period of time (due to different grades, different student abilities, different levels of knowledge, different tutors need different levels of guidance, project time periods will be different) give students the opportunity to learn independently, and ultimately form a viable output or display (this step Is the basis for evaluation). PBL is an effective way to dig deep learning ability. In today's classroom, we often hear the question: "Why should we learn?" "Why do we want to do this?" The students felt that class was both boring and meaningless. In the PBL, students are able to participate in meaningful research that is of interest to them. The authenticity of PBL activities motivates students and enhances the value of their learning. The students decide how to solve the problem and the activities or processes that must be performed to complete the task. Compared to the knowledge gained in traditional classrooms, students are more likely to remember textbook knowledge because they are actively involved in the project. Students who gain knowledge through PBL can apply what they have learned to real-life situations. The traditional teaching mode pays attention to the passive teaching of concepts and framework knowledge. This teaching mode can no longer meet the rapid changes of today, and the uncertain society demands students. The basic knowledge and skills can no longer meet the needs of society. In this social context, the education standards of developed countries in Europe and the United States have clearly stated that it is necessary to link theory with practice, emphasize the practical application of textbook content, and require students to work independently, rationally think, lifelong learning, and cultivate and develop competitiveness in the 21st century. Although PBL is highly regarded, it has not been implemented in most schools. The rate of progression and the demand for points are the two main drivers of the current traditional teaching model. Many factors are directly linked to these two main causes, such as: promotion, teacher evaluation, school ranking, performance salary, etc. I believe that almost every educator supports deep learning activities. Although PBL promotes deep learning, the problem is that it takes a lot of time. Because the exam does not involve these abilities, teachers are reluctant to accept PBL and 21st century skills development, and are not willing to prepare lessons or teach for these teaching methods. How to do it? My idea is to use PBL as a powerful aid to traditional educational methods, not revolutionaries. While pursuing PBL inquiry learning, it still pays attention to traditional teaching methods. According to different grades and different disciplines, the PBL project is divided into three grades and two categories (required and expanded). details as follows: Level I is a short-term project (category: necessary items). This type of project is based on the content of the course. Each semester, students must complete core subjects (such as “Material Science, Life Science, Earth and Universe Science, Engineering and Technology†in the 2017 Compulsory Primary School Science Curriculum Standards). The level I inquiry activities are mainly based on curriculum learning. The role of teachers is mainly to supervise and guide students to achieve successful learning outcomes. In the process, teachers will challenge and expand students' understanding of concepts and skills, so that students can gain a deeper and broader understanding through new experiences, gain more information, improve their skills, and apply their concepts through other activities. Understanding. The I-level short-term project mainly helps the students to understand the framework concept knowledge more realistically through the PBL method. It is based on the group of 3-4 people. (To ensure the time and progress requirements, the students should complement each other, and the students themselves can adopt the dismissal system, redemption The system and the voting system ensure that the team works effectively. In the course, students will receive the documentation needed to train and solve the project at the beginning of each school year. In order to ensure the smooth completion of the project, teachers will provide timely guidance and feedback. The I-level project is designed according to the 5E teaching model (introduction, inquiry, interpretation, migration and evaluation). During the implementation process, students will learn to summarize the questionnaire design, questionnaire survey, data analysis and results. Students are cooperative, self-evaluating and responsible for their own learning. Levels II and III are academic year projects (category: expansion projects). This type of project is an interdisciplinary project. It mainly examines students' ability to transfer and transform knowledge. These two types of projects are set up for students who have the ability to learn and develop in the direction of their own interests, who like to create, want to conduct their own research, and develop their own products. Can be initiated in the fields of physics and mathematics, physics and chemistry, engineering and technology. Level II projects are aimed at students who have difficulties in spontaneously guiding problems in their own independent development projects. Level III projects are suitable for students who are almost self-developed from start to finish who do not need teacher assistance. At all stages of Level II and Level III projects, teachers should guide students in a timely manner to provide the necessary assistance and to provide feedback. The results achieved by students in Level II and Level III projects should be exhibited in scientific exhibitions and related science competitions. In the I-level project, the goal is to lay a solid foundation for more in-depth projects and develop certain skills through a “teacher-assisted†and structured environment. Level II projects are semi-structured, with teachers leading out activities at the initial stage and supervising and mentoring students. After that, the students will ask more guiding questions and achieve the final results. Level III activities are completely student-led and require little teacher assistance. For each level of project completion, students must produce digital results to demonstrate the evaluation. Towel Racks,Wall Towel Rack,Vertical Towel Rail,Bathroom Towel Rack Kaiping Yufa Sanitary Ware Co.,ltd , https://www.jmyufafaucets.com