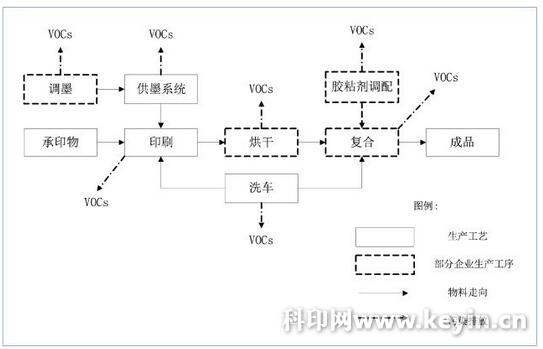
Volatile organic compounds, VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds), literally refer to organic compounds that are volatile under certain conditions. Volatile organic compounds have a certain impact on human health and the environment. There are several definitions according to the influence and control objects. For example, the US ASTM D3960-98 standard defines VOCs as any organic compound that can participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions. Definition of the US Federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Volatile organic compounds are any carbon compounds that participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions except CO, CO2, H2CO3, metal carbides, metal carbonates, and ammonium carbonate. The World Health Organization (WHO, 1989) defines TVOC as the general term for volatile organic compounds with melting points below room temperature and boiling points between 50 ° C and 260 ° C. The definitions of VOCs in the international standard ISO4618 / 1-1998 and the German DIN55649-2000 standard for general terms of paint and varnish are: in principle, any organic liquid and / or solid that can spontaneously develop at normal temperature and pressure. At the same time, the German DIN55649-2000 standard makes a limit when determining the content of VOCs, that is, any organic compound with a boiling point or initial boiling point lower than or equal to 250 ° C under normal pressure conditions. In terms of environmental protection, VOCs are the key prerequisites for PM2.5 and O3 pollution. Therefore, the purpose of defining VOCs is very clear, in order to control air pollution, the definitions of VOCs in China are different, but the basic principles are the same. Definition: Organic compounds that participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions or organic compounds determined by measurement or accounting according to prescribed methods. VOCs used for accounting or filing refer to organic compounds with a boiling point of not less than 10 Pa at 20 ° C or a boiling point of not higher than 260 ° C at standard atmospheric pressure of 101.325 KPa (or organic compounds with corresponding volatility under actual production conditions), except methane, The content of non-methane total hydrocarbons (NMHC, Non-Methane HydroCarbon) is also used as the detection and control index. The printing industry uses a lot of inks, thinners, fountain solutions, adhesives, coating fluids, varnishes, car wash water, etc. in the production process. These raw and auxiliary materials basically contain organic solvents that meet the definition of VOCs, and in the production process Emissions to the atmosphere, therefore, as a key industry for VOCs control. Typical printing process VOCs generation and emission nodes, see Figure 1. Figure 1 Typical printing process VOCs generation and emission nodes According to the measured data of Shanghai Academy of Environmental Sciences, the untreated exhaust VOCs (characterized by NMHC) of typical plastic film solvent-type gravure discharge ports are 300 ~ 600mg / m³; the typical dry composite exhaust port untreated exhaust gas VOCs (characterized by NMHC) even reach 3500mg / m³; typical sheet-fed offset printing outlet untreated exhaust VOCs (characterized by NMHC) are 30 ~ 100mg / m³; typical water-based flexographic outlet untreated exhaust VOCs ( Characterized by NMHC) 10 ~ 50mg / m³ (refer to Shanghai “Printing Industry Air Pollutant Emission Standards†(DB31 / 872-2014), NMHC emission limit is 50mg / m³.) With the advancement of VOCs emission reduction work, various regions have successively issued corresponding control policies to manage and control VOCs emissions from the printing industry. 1 Formulate VOCs emission standards and VOCs emission reduction technical specifications Up to now, Guangdong, Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Sichuan, Chongqing, Hebei and Shandong have issued local printing industry or related emission standards. The standard generally specifies organized emission standards for pollution sources (chimneys), which are characterized by total non-methane total hydrocarbons and total VOCs; stipulates the plant boundary concentration limit standards, which are characterized by total non-methane total hydrocarbons and total VOCs; , Characterized by non-methane total hydrocarbons. In 2018, the state will introduce emission standards for the printing industry. At that time, the printing industry across the country will have an up-to-date emission standard. The successive introduction of standards can also be seen from the side, the emission of VOCs in the printing industry is indeed a problem. In order to cooperate with the implementation of the standard, Shanghai formulated the "Technical Guidelines for the Treatment of Volatile Organic Compounds in the Printing Industry" in 2016. According to different printing processes, the guide provides suggestions on VOCs emission reduction in terms of source, process, management, and end treatment. Similar documents have been issued in other provinces and cities. Lint remover:
Hair ball trimmer is mostly rotary knife head, high sharpness, rapid shaving hair ball. Equipped with honeycomb mesh cover, easy to pick up all kinds of hair ball, and quickly shave off part of hair ball trimmer equipped with independent suction ball wheel, will not make the dandruff flying around
sample:
A good sweater (cotton-padded coat, sweater, woolen clothes or coat), for any reason (mixed with other clothes, or stuck to the pilling on the quilt) gets stuck to the annoying wool balls. Dear friend, has this happened to you? The Lint remover can help.
Lint remover has different call in different place, if Fuzz shaver, Fabric Shaver, it is a kind of small home appliance that designs hair ball for purify clothings surface specially what includes Electric Lint Remover and Washable Lint Remover. Besides clip wool ball, still can suck the dirt such as sundry inside sweater.
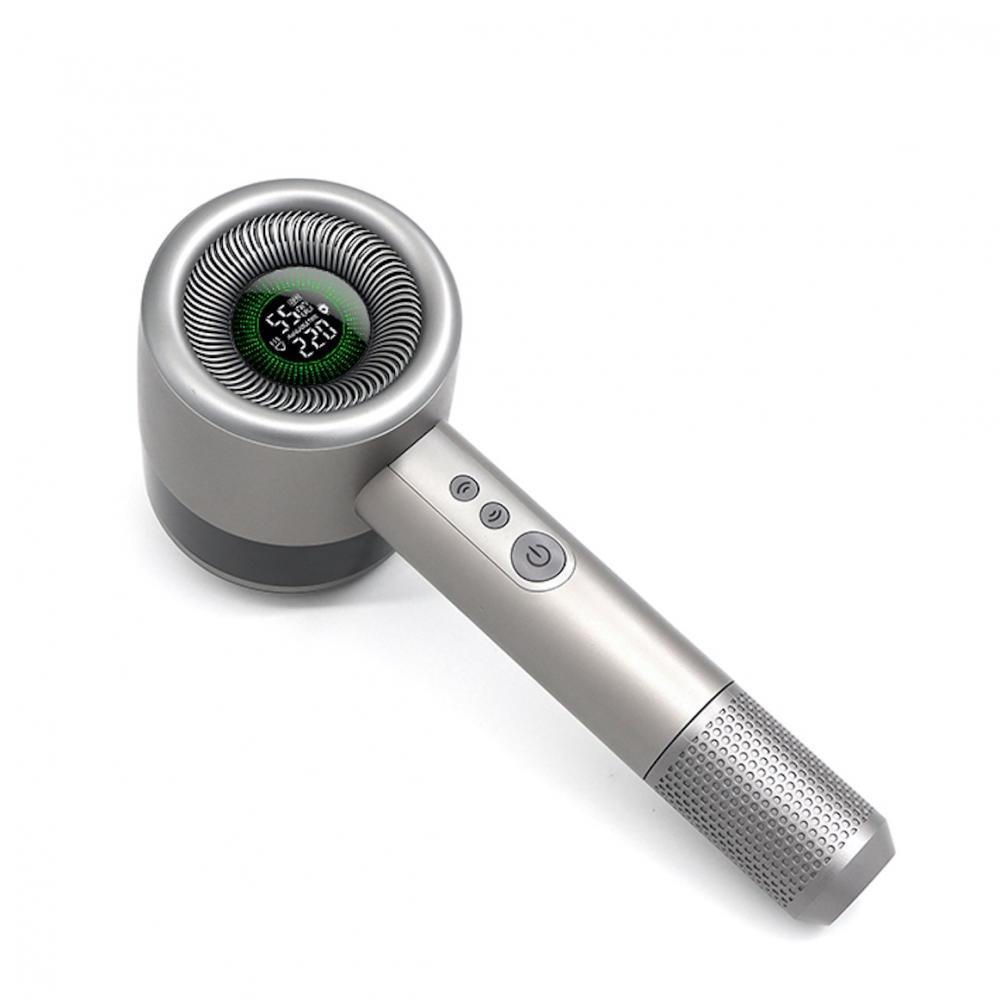
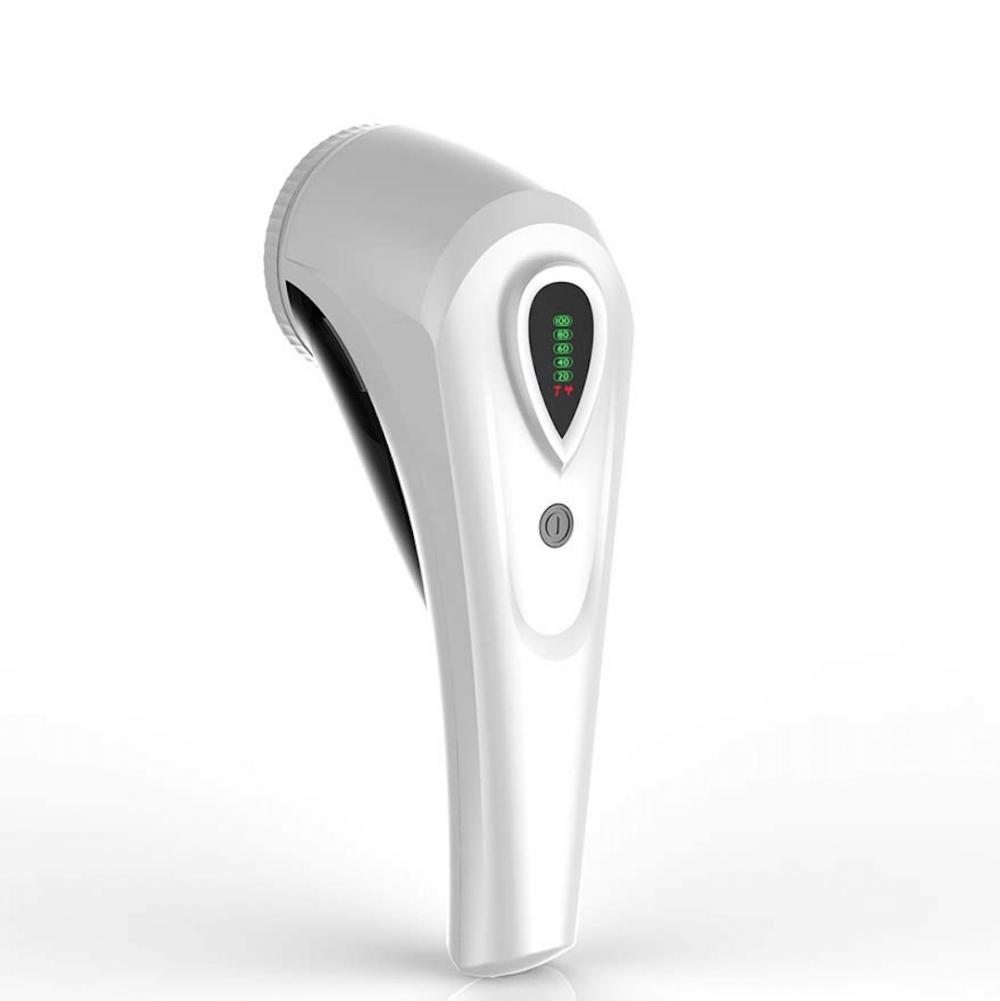
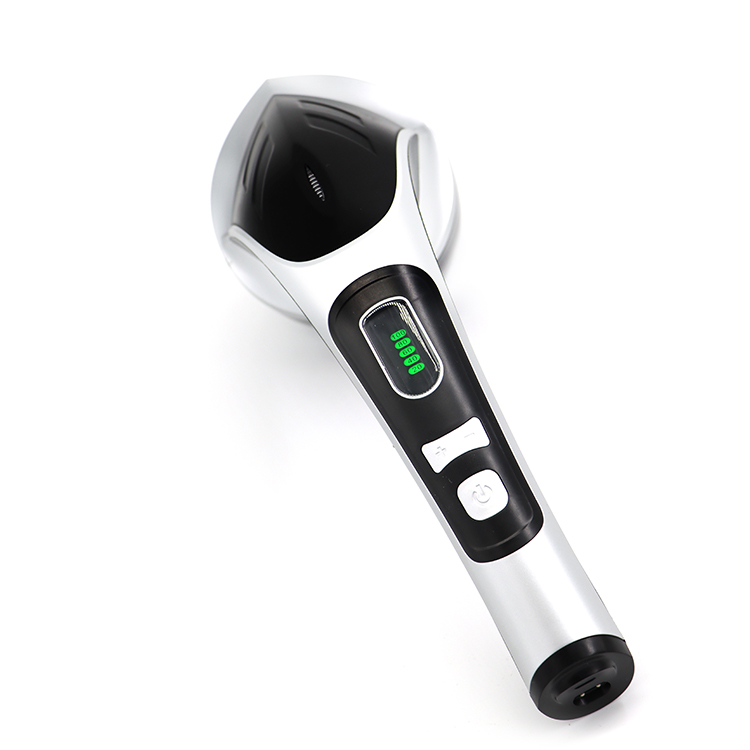
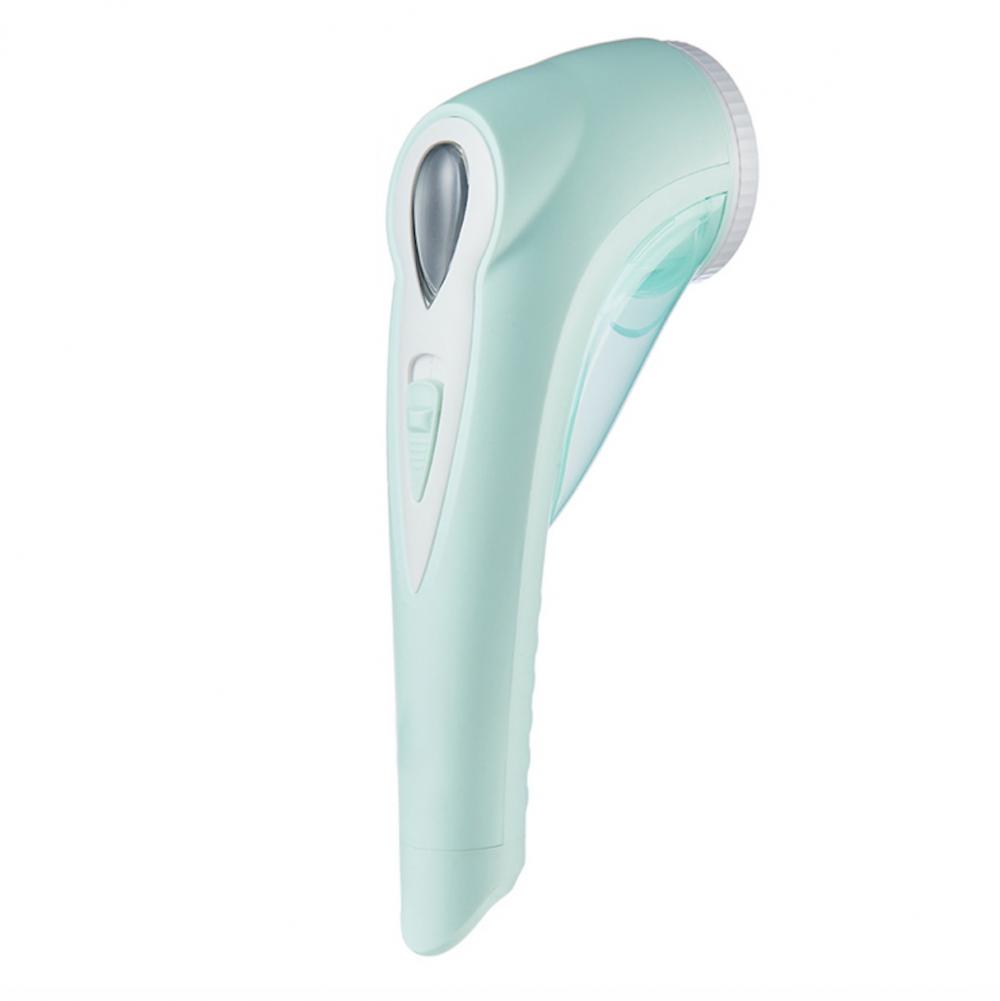




Lint Remover,Fuzz Shaver,Pilling Remover Lint Shaver,Household Electric Lint Remover
Ningbo Beilun Xuanfeng Molding Co., Ltd. , https://www.schelfern.com